The COMPOHOSE® Advantage
COMPOHOSE®: Enhancing Safe Fluid Transfer
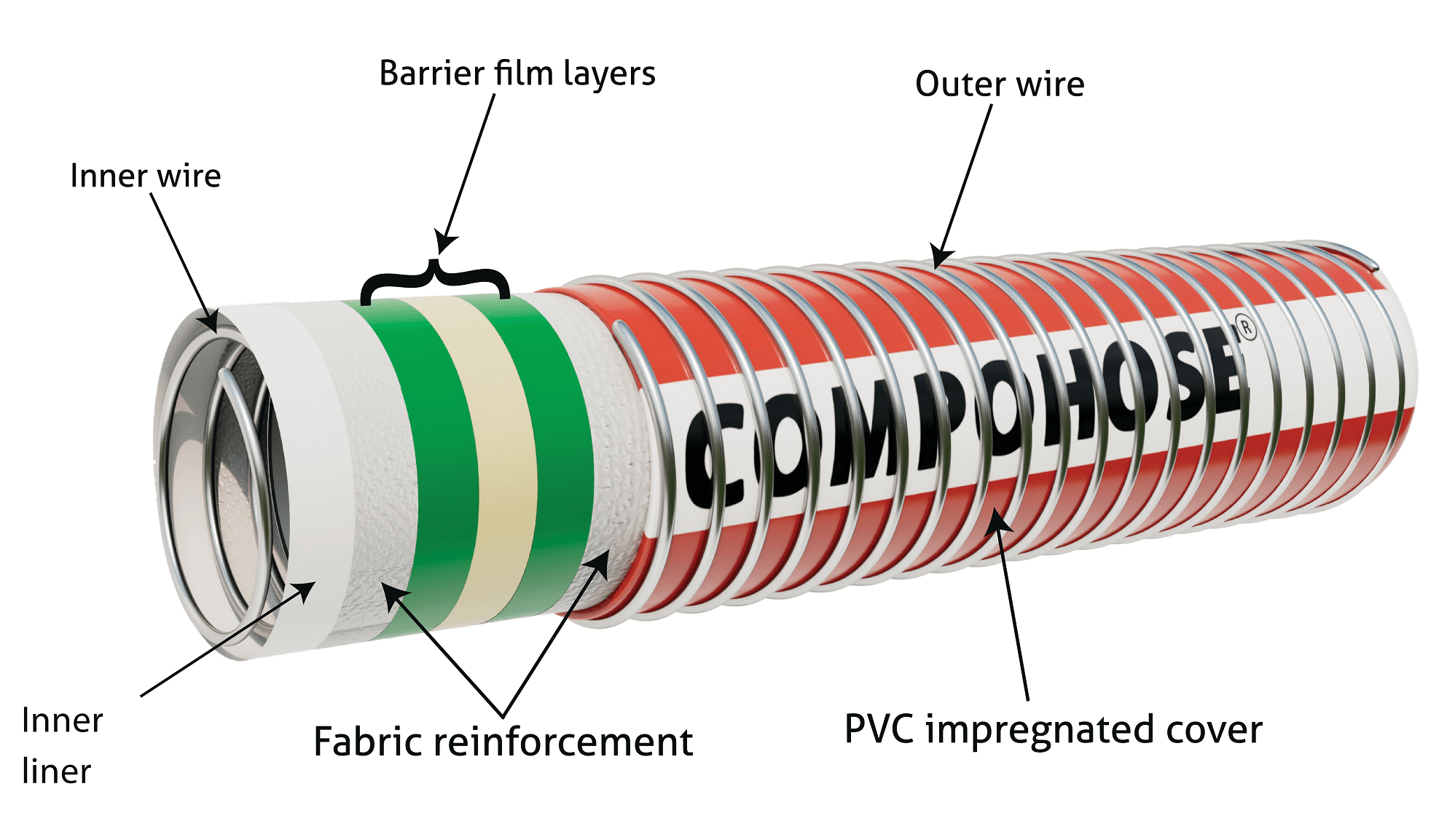
COMPOHOSE® Construction
COMPOSHOSE® are flexible hoses designed to handle a wide range of fluids, chemical transfers, and cryogenic applications. They are made using multiple layers of different materials, each adding to the hose’s overall performance and durability. Here’s how they are built:
Inner Wire Helix
The innermost part is a wire helix made from corrosion-resistant metal like galvanized steel, stainless steel, or polypropylene-covered wire. This helix provides structural support and prevents the hose from collapsing under pressure or vacuum.
Inner Layer
Over the wire helix, a layer of thermoplastic material is applied to protect against the chemicals in the fluid and prevent leaks or absorption. This layer provides axial strength and greater tensile strength.
Reinforcement Layers
Composite hoses have multiple reinforcement layers made from textile fabrics, woven fabrics, or synthetic materials. These layers improve the hose's strength, flexibility, and ability to withstand pressure. PTFE liners are available to handle more aggressive chemicals.
Barrier Layer
A barrier layer may be added to further enhance chemical resistance and prevent fluid permeation or absorption. This layer is typically made from chemically resistant polymeric films. It is unaffected by 100% aromatics and prevents permeation by polar and non-polar liquids.
Outer Layer
The outer layer is made from abrasion-resistant materials like PVC thermoplastics. This layer protects the hose from external damage, environmental factors, and UV radiation, also contributing to the overall appearance of the hose.
External Wire Helix
An external wire helix is added over the outer layer to provide additional hoop strength and protection against crushing or bending. This coil also ensures double electrical continuity in harsh environments.
Externally Swaged/Crimped End Fittings
The hose ends are fitted with connectors or couplings made from materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, or other alloys. These fittings allow the hose to be connected securely to fluid sources and destinations.
The exact construction process varies by manufacturer and hose requirements. The layers are assembled using specialized machinery that applies pressure to bond them together. Quality control measures, like pressure testing and visual inspections, ensure the hose’s integrity. Composite hoses are highly customizable to suit different applications, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Abbreviations for Product Types
1st letter
Inner wire
A : Aluminium, G : Galvanised Steel, S : Stainless steel (SS304 / SS316), P : PP Coated wire/ PVDF Coated wire
2nd letter
Inner linings (Carcass)
T : PTFE, F : Fiberglass Fabric R: Nitrile Rubber
3rd letter
Outer wire
A : Aluminium, G : Galvanised Steel, S : Stainless steel (SS304 / SS316), P : PP Coated wire.
Multifaceted Applications
Ship-to-Shore Transfer
Efficiently loads and unloads hydrocarbons, chemicals, and cryogenic fluids between vessels and ports.
Ship-to-Ship Transfer
Facilitates safe fluid transfer between ships, essential for maritime logistics.
Road-Rail Tanker Transfer
Aids in transferring fluids between road/rail tankers and storage facilities.
In-Plant Jumper Connections
Functions as flexible connections within industrial plants, accommodating movement while ensuring secure fluid transfer.
Manifold Connections
Ensures precise fluid distribution and collection across manifold systems.
Drum Filling and General Transfer
Essential for filling drums and general fluid transfer tasks, minimizing wastage and maximizing safety.



